In the rapidly evolving landscape of today’s organizations, adaptability and agility have become more than just buzzwords; they are essential for survival and growth. The traditional approach of executing projects on an ad hoc basis is giving way to a strategic imperative—building change management maturity. This shift is not merely a choice but a compelling competitive advantage.
Recent statistics underscore the urgency of this change. According to a survey by Gitnux, more than 80% of businesses face increasing pressure to adapt to market forces, including technological advancements and evolving customer expectations. In this environment, mature organizations can respond swiftly to market dynamics and implement strategic initiatives with unparalleled precision and speed.
Two prominent models have emerged as guiding beacons in this transformative journey: the Change Management Institute (CMI) Change Maturity Model and Prosci’s Change Management Maturity Model. Both models are deeply entrenched in the concept of organizational competency levels, offering a structured framework comprising five progressive maturity levels.
In this article, we will embark on an enlightening journey, exploring the foundations of these two prominent change management maturity models, uncovering their intricacies, and paving the way for a more holistic approach to change management. Additionally, we will delve into the critical role of various organizational functions, shedding light on how they can actively contribute to the organization’s change maturity.
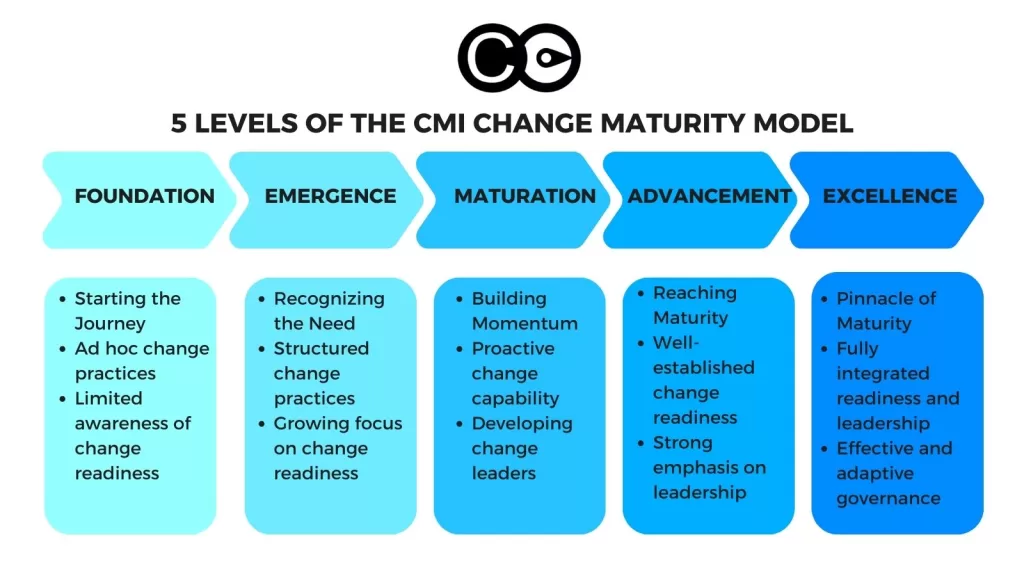
CMI Change Maturity Model
The Change Management Institute (CMI) Change Maturity Model is a comprehensive framework that takes a holistic approach to enhancing an organization’s change management maturity. It’s divided into three core functional domains, each playing a vital role in the overall journey toward maturity: Project Change Management, Business Change Readiness, and Strategic Change Leadership. These domains serve as the foundation for achieving higher levels of maturity within the organization.
Within each of these domains, the CMI model outlines a structured path, consisting of five distinct maturity levels. These levels represent a continuum, starting at Level 1, which serves as the foundational stage, and progressing all the way to Level 5, the zenith of maturity and effectiveness. This multi-tiered approach offers organizations a clear roadmap for growth and development, ensuring that they have the tools and insights necessary to navigate the complexities of change management.
The distinguishing feature of the CMI model is its emphasis on the idea that true change maturity extends beyond the realm of project execution. While executing individual projects is undoubtedly important, the CMI model advocates for a broader perspective. It recognizes that sustainable change maturity relies on the cultivation of readiness for change across the entire organization. This involves preparing teams, leaders, and employees to adapt to and embrace change seamlessly, making it an integral part of the organizational culture.
Furthermore, the CMI model underscores the indispensable role of change leadership and governance in nurturing change maturity. Effective leadership is the driving force behind successful change initiatives, and it’s the cornerstone of achieving higher levels of maturity. Governance structures ensure that change management practices are not just theoretical concepts but are woven into the fabric of how the organization operates on a day-to-day basis. Governance provides the necessary framework for sustaining change maturity in the long run.
Prosci Change Maturity Model
In contrast to the more specific functional domains emphasized by the CMI model, the Prosci Change Maturity Model takes a broader perspective, focusing on the development of overall organizational change management competency. Rather than zeroing in on individual functions, it provides a generic framework that covers key areas integral to building change maturity. These areas include:
Project Execution: The model places a strong emphasis on effective project execution as a cornerstone of change management maturity. It recognizes that the successful implementation of change initiatives hinges on well-executed projects, including detailed planning and efficient execution.
Business Capability and Readiness: Understanding the readiness and capability of the organization is another critical component. The Prosci model highlights the significance of assessing an organization’s readiness to undergo change, including the ability to adapt to new strategies, technologies, and processes.
Senior Change Leadership: Leadership is vital in steering the organization toward maturity. The model underlines the importance of senior change leadership, emphasizing that leaders play a pivotal role in setting the tone for change, championing initiatives, and fostering a culture of adaptability.

Formalized Practices and Organizational Awareness
One of the key drivers for elevating maturity, according to the Prosci model, is the establishment of formalized change management practices. This includes developing and implementing standardized methodologies to ensure consistent change management approaches across the organization. Furthermore, the model advocates for creating widespread organizational awareness about the significance of change management and its role in achieving successful outcomes.
The Role of Change Management Training
A cornerstone of the Prosci model’s approach to maturity is the incorporation of comprehensive change management training. This training equips individuals within the organization with the knowledge and skills needed to effectively manage change initiatives. It emphasizes the importance of investing in the development of internal change management expertise.
While both the CMI and Prosci models address the critical areas of project, business, and change leadership in driving change maturity, they diverge in their approaches. The CMI model offers a broader perspective, highlighting the importance of agility and continuous improvement as essential components of maturity. It places a strong emphasis on crafting the right cadence, establishing efficient business processes, and implementing robust governance practices. In contrast, the Prosci model, while equally comprehensive, provides less specific guidance on embedding change practices within the organization’s fabric and processes. Instead, it places a strong focus on the effective implementation of change initiatives.
What’s Missing in Current Change Maturity Models?
The lacuna in existing change maturity models becomes evident when we consider the need to genuinely embed change management principles and practices within an organization’s DNA. True integration transcends the mere execution of initiatives and building change capabilities among leaders and employees. It calls for collaboration across multifarious functions, including Risk Management, Marketing, Strategy, and Human Resources, to engrain change principles and practices. The focus is on holistic change capability, encompassing different functional areas. This approach fosters a culture where practices, capabilities, and supporting structures converge to enable continuous change.
In the following sections, we’ll explore examples of how change management principles and practices can be applied across seven key functions: Risk Management, Strategy and Planning, Operations, Project Management, Human Resources, Technology, and Marketing.
1. Risk Management
Change management principles and practices can enhance risk management by offering valuable insights into change-related risks. Risk professionals can leverage change management analytics to assess data-based risk factors, such as business readiness indicators and the potential impact of changes on the organization and its customers. Armed with this data, risk professionals can make informed assessments, helping the organization better understand risk profiles and make well-informed decisions.
2. Strategy and Planning
Strategic planning should not only focus on industry trends and financial data but also incorporate change capability assessments. Considerations should include the availability of change leadership talent, the organization’s capacity for executing change, and the historical performance related to change volume and velocity. The strategic roadmap should integrate historical data on change impact volumes and execution, enabling effective planning. Supporting structures and processes, including governance, reporting, and communities of practice, should be designed to ensure successful change execution.
3. Operations
Operations is a core domain for change management. This function offers numerous opportunities for applying change best practices. It involves building change management capabilities in employees and managers, enhancing employee engagement channels, and facilitating effective learning and development. With the right change data and analytics, Operations can strategically plan business delivery by making predictive assessments of performance based on projected change impacts. The key lies in systematically integrating analysis and decision-making processes within the operating cadence.
4. Project Management
This is the most familiar territory for change management. Many organizations have dedicated change managers responsible for project delivery. The conventional practices of change management, including capability building, change methodologies, portfolio management, and project delivery, are all part of the project management function.
5. Human Resources
Human Resources often plays a central role in supporting the people side of change. The function includes building change management capabilities as part of learning and development efforts. However, there’s substantial value in managing restructuring initiatives as change projects, and adhering to structured change management practices. This structured approach ensures that affected stakeholders are appropriately engaged, and processes, systems, and supporting structures impacted by change are meticulously mapped.
6. Technology
Change management is not limited to large projects; it extends to technology changes that impact stakeholders and users. Even smaller technology initiatives can benefit from the application of change management principles. Change management analytics can facilitate better technology releases and deployments. By considering change impact data, organizations can plan technical releases more effectively, taking into account organizational impacts.
7. Marketing and Customer Experience
Change management practices can play a pivotal role in marketing and customer experience functions. Customer change impacts, such as external positioning and alignment with customer needs, should be integral to marketing campaigns, product launches, and communications. These practices, including impact assessment, change analytics, and change planning, enable organizations to deliver what they promise to customers.
In closing, the true value of change maturity emerges when it becomes a part of various organizational functions. It’s not just about developing isolated methodologies or supporting initiative delivery; it’s about becoming an organization where change is seamlessly integrated into every facet.
Ready to Elevate Your Change Maturity?
The journey to achieving a higher level of change maturity begins with holistic integration within your organization. If you’re interested in exploring how The Change Compass can help you in this transformative process, we invite you to book a weekly demo with us.
Book Your Weekly Demo with The Change Compass and embark on your path toward comprehensive change management maturity.






